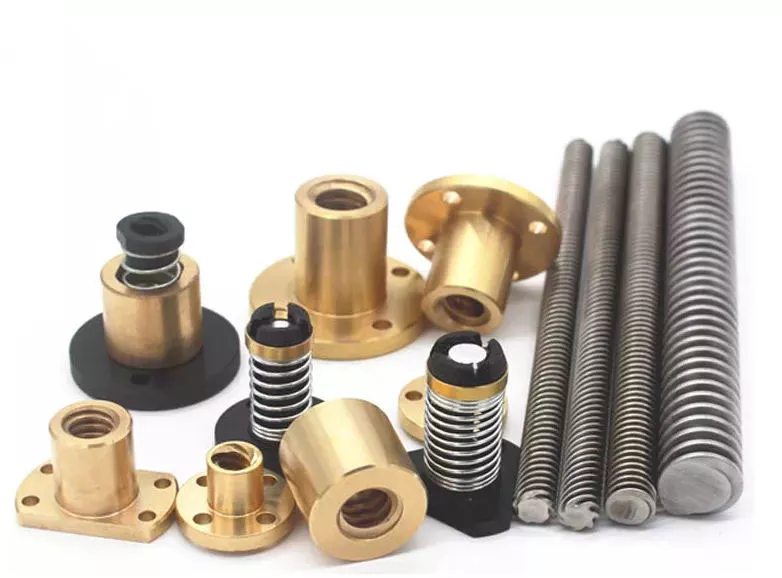
Product Description
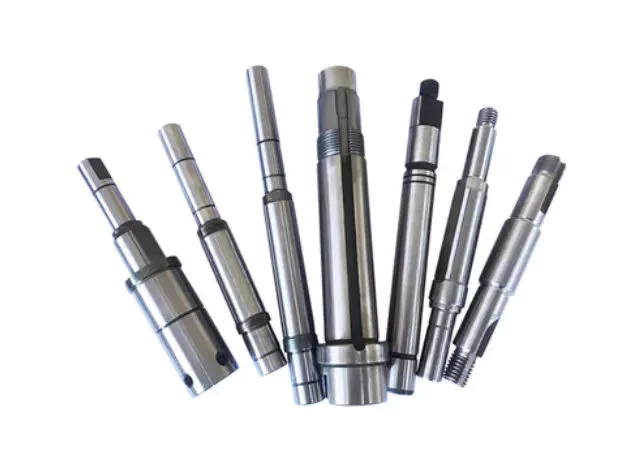
Adapter Sleeves, Withdrawal Sleeves H308 H208 H2308 H320 H218 H209 H309 H210 H310 Equivalent CZPT CZPT KOYO NACHI
Adapter sleeve with various sizes
ISO9001 & IENET certificate approved
OEM accepted
Competitive price, good quality, stock
Adapter sleeves are used for securing tapered bore bearings on to the cylindrical shafts, it easy mounting and dismounting
1. Adapter sleeves are used for securing tapered bore bearings on to the cylindrical shafts. They facilitate easy mounting and dismounting. They are suitable for both smooth and stepped shafts. The sleeves can easily adapt to the shaft diameter.
2. The adapter sleeves have slotted design and an external taper. They are usually not surface treated but oiled and are supplied with a lock nut and a locking device. They have an oil duct, distribution groove, and a threaded side. For stepped shafts, they have 2 supply ducts and distribution grooves on the outer surface.
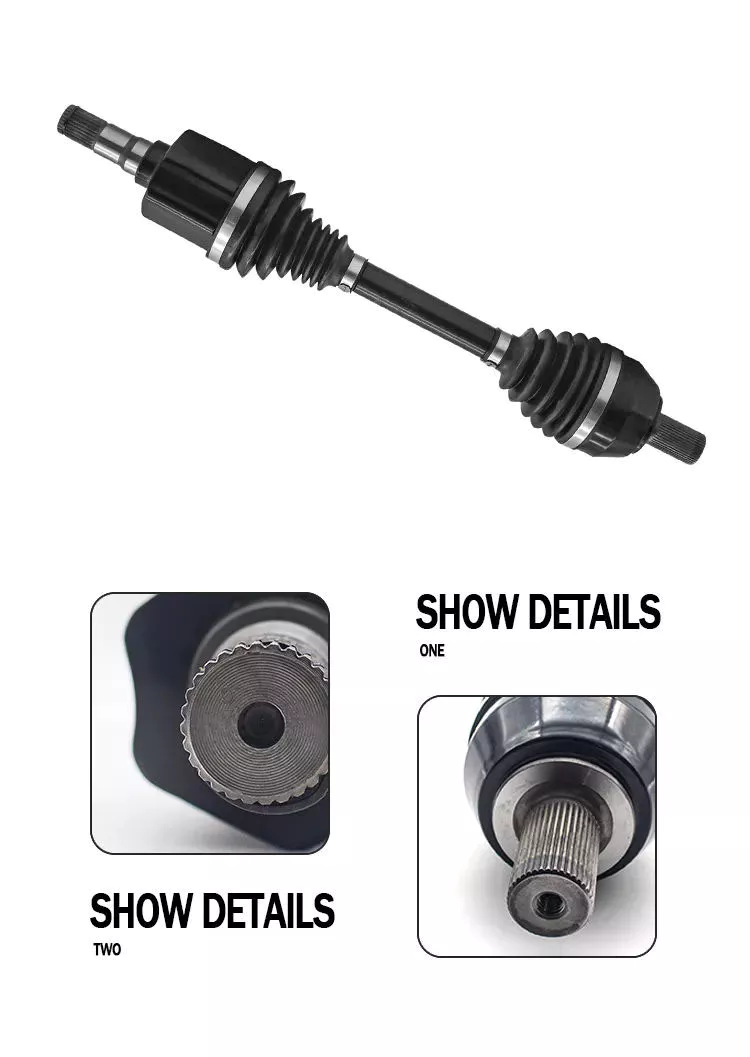
3. Withdrawal sleeves are used for mounting tapered bearings on to the cylindrical shafts. They facilitate easy mounting, securing and dismounting. They are suitable for both smooth and stepped shafts. Bearing sleeve can easily adapt to the shaft diameter. They are usually coated with a preservative, are slotted and have an external taper. This allows the sleeve to be used with wide spherical roller bearings. Withdrawal sleeves for oil injection have oil ducts and distribution grooves, on the threaded side.
4. We supply the Adapter Sleeves in accordance with ISO H3/1-1979, both Metric and Inch.
Adapter Sleeve (H200):
H204, H205, H206, H207, H208, H209, H210, H211, H212,
H213, H214, H215, H216, H217, H218, H219, H220, H221,
H222
Adapter Sleeve (H300):
H304, H305, H306, H307, H308, H309, H310, H311, H312,
H313, H314, H315, H316, H317, H318, H319, H320, H321,
H322
Adapter Sleeve (H3100):
H3120, H3122, H3124, H3126, H3128, H3130, H3132,
H3134, H3136, H3138, H3140, H3144, H3148, H3152,
H3156, H3160, H3164, H3168, H3172, H3176, H3180,
H3184, H3188, H3192, H3196
Adapter Sleeve (H3000):
H3571, H3026, H3571, H3030, H3032, H3034, H3036,
H3038, H3040, H3044, H3048, H3052, H3056, H3060,
H3064, H3068, H3072, H3076, H3080, H3084, H3088,
H3092, H3096
Adapter Sleeve ( H2300 ):
H2304, H2305, H2306, H2307, H2308, H2309, H2310,
H2311, H2312, H2313, H2314, H2315, H2316, H2317,
H2318, H2319, H2320, H2321, H2322, H2324, H2326,
H2328, H2330, H2332, H2334, H2336, H2338, H2340,
H2344, H2348, H2352, H2356
Detailed Models:
| Designation |
Principal dimensions |
| d1 |
d |
d2 |
B1 |
B2 |
| mm |
| H304 |
17 |
20 |
32 |
28 |
7 |
| H305 |
20 |
25 |
38 |
29 |
8 |
| H306 |
25 |
30 |
45 |
31 |
8 |
| H307 |
30 |
35 |
52 |
35 |
9 |
| H308 |
25 |
40 |
58 |
36 |
10 |
| H309 |
40 |
45 |
65 |
39 |
11 |
| H310 |
45 |
50 |
70 |
42 |
12 |
| H311 |
50 |
55 |
75 |
45 |
13 |
| H312 |
55 |
60 |
80 |
47 |
14 |
| H313 |
60 |
65 |
85 |
50 |
15 |
| H315 |
65 |
75 |
98 |
55 |
16 |
| H316 |
70 |
80 |
105 |
59 |
17 |
| H317 |
75 |
85 |
110 |
63 |
18 |
| H318 |
80 |
90 |
120 |
65 |
18 |
| H319 |
85 |
95 |
125 |
68 |
19 |
| H320 |
90 |
100 |
130 |
71 |
20 |
| H321 |
95 |
105 |
140 |
74 |
20 |
| H322 |
100 |
110 |
145 |
77 |
21 |
Our Company
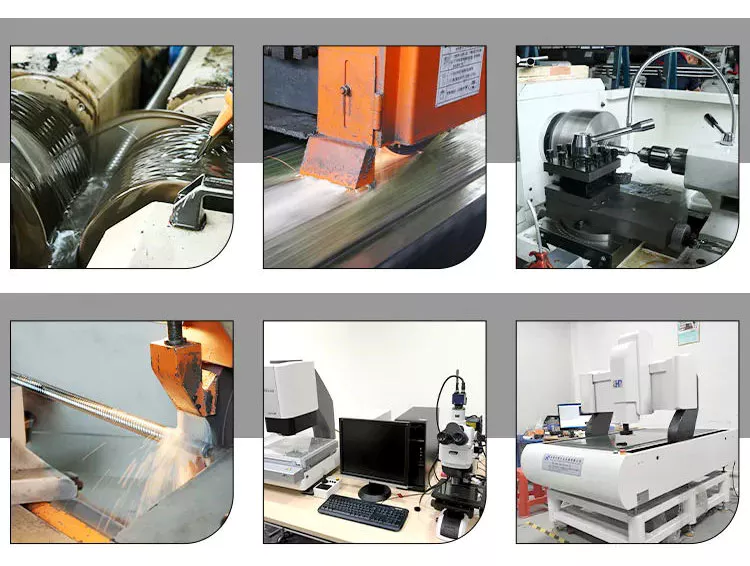
As a comprehensive industrial enterprise that integrates R & D and sales services, with over 20 years’ experience, especially the guaranteed supplier of China Manufacturing Network, our factory covers an area of 10,000 square meters, which enables very quick delivery.
Owning the most advanced CNC automatic production line, automatic assembly line, and a varied of testing equipment, our bearings mainly cover SKF, NSK, NTN, KOYO, TIMKEN, NACHI, THK etc., which meets all low noise, low vibration, low friction, high precision, high sealed, high turning speed and long life requests.
Exhibition:
FAQ
SAMPLES
1.Samples quantity: 1-10 pcs are available.
2.Free samples: It depends on the model NO., material and quantity. Some of the bearings samples need client to pay samples charge and shipping cost.
3.It’s better to start your order with Trade Assurance to get full protection for your samples order.
CUSTOMIZED
The customized LOGO or drawing is acceptable for us.
MOQ
1.MOQ: 10 pcs mix different standard bearings.
2.MOQ: 5000 pcs customized your brand bearings.
OEM POLICY
1.We can printing your brand (logo,artwork)on the shield or laser engraving your brand on the shield.
2.We can custom your packaging according to your design
3.All copyright own by clients and we promised don’t disclose any info.
SUPPORT
Please visit our 1Xihu (West Lake) Dis.in bearings website, we strongly encourage that you can communicate with us through email, thanks!
What Are Screw Shaft Threads?
A screw shaft is a threaded part used to fasten other components. The threads on a screw shaft are often described by their Coefficient of Friction, which describes how much friction is present between the mating surfaces. This article discusses these characteristics as well as the Material and Helix angle. You’ll have a better understanding of your screw shaft’s threads after reading this article. Here are some examples. Once you understand these details, you’ll be able to select the best screw nut for your needs.

Coefficient of friction between the mating surfaces of a nut and a screw shaft
There are 2 types of friction coefficients. Dynamic friction and static friction. The latter refers to the amount of friction a nut has to resist an opposing motion. In addition to the material strength, a higher coefficient of friction can cause stick-slip. This can lead to intermittent running behavior and loud squeaking. Stick-slip may lead to a malfunctioning plain bearing. Rough shafts can be used to improve this condition.
The 2 types of friction coefficients are related to the applied force. When applying force, the applied force must equal the nut’s pitch diameter. When the screw shaft is tightened, the force may be removed. In the case of a loosening clamp, the applied force is smaller than the bolt’s pitch diameter. Therefore, the higher the property class of the bolt, the lower the coefficient of friction.
In most cases, the screwface coefficient of friction is lower than the nut face. This is because of zinc plating on the joint surface. Moreover, power screws are commonly used in the aerospace industry. Whether or not they are power screws, they are typically made of carbon steel, alloy steel, or stainless steel. They are often used in conjunction with bronze or plastic nuts, which are preferred in higher-duty applications. These screws often require no holding brakes and are extremely easy to use in many applications.
The coefficient of friction between the mating surfaces of t-screws is highly dependent on the material of the screw and the nut. For example, screws with internal lubricated plastic nuts use bearing-grade bronze nuts. These nuts are usually used on carbon steel screws, but can be used with stainless steel screws. In addition to this, they are easy to clean.
Helix angle
In most applications, the helix angle of a screw shaft is an important factor for torque calculation. There are 2 types of helix angle: right and left hand. The right hand screw is usually smaller than the left hand one. The left hand screw is larger than the right hand screw. However, there are some exceptions to the rule. A left hand screw may have a greater helix angle than a right hand screw.
A screw’s helix angle is the angle formed by the helix and the axial line. Although the helix angle is not usually changed, it can have a significant effect on the processing of the screw and the amount of material conveyed. These changes are more common in 2 stage and special mixing screws, and metering screws. These measurements are crucial for determining the helix angle. In most cases, the lead angle is the correct angle when the screw shaft has the right helix angle.
High helix screws have large leads, sometimes up to 6 times the screw diameter. These screws reduce the screw diameter, mass, and inertia, allowing for higher speed and precision. High helix screws are also low-rotation, so they minimize vibrations and audible noises. But the right helix angle is important in any application. You must carefully choose the right type of screw for the job at hand.
If you choose a screw gear that has a helix angle other than parallel, you should select a thrust bearing with a correspondingly large center distance. In the case of a screw gear, a 45-degree helix angle is most common. A helix angle greater than zero degrees is also acceptable. Mixing up helix angles is beneficial because it allows for a variety of center distances and unique applications.
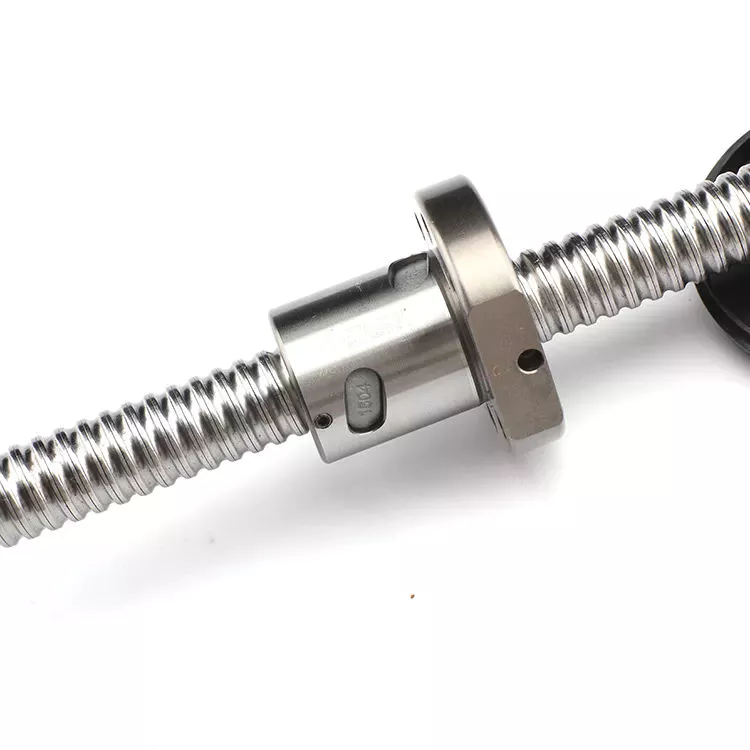

Thread angle
The thread angle of a screw shaft is measured from the base of the head of the screw to the top of the screw’s thread. In America, the standard screw thread angle is 60 degrees. The standard thread angle was not widely adopted until the early twentieth century. A committee was established by the Franklin Institute in 1864 to study screw threads. The committee recommended the Sellers thread, which was modified into the United States Standard Thread. The standardized thread was adopted by the United States Navy in 1868 and was recommended for construction by the Master Car Builders’ Association in 1871.
Generally speaking, the major diameter of a screw’s threads is the outside diameter. The major diameter of a nut is not directly measured, but can be determined with go/no-go gauges. It is necessary to understand the major and minor diameters in relation to each other in order to determine a screw’s thread angle. Once this is known, the next step is to determine how much of a pitch is necessary to ensure a screw’s proper function.
Helix angle and thread angle are 2 different types of angles that affect screw efficiency. For a lead screw, the helix angle is the angle between the helix of the thread and the line perpendicular to the axis of rotation. A lead screw has a greater helix angle than a helical one, but has higher frictional losses. A high-quality lead screw requires a higher torque to rotate. Thread angle and lead angle are complementary angles, but each screw has its own specific advantages.
Screw pitch and TPI have little to do with tolerances, craftsmanship, quality, or cost, but rather the size of a screw’s thread relative to its diameter. Compared to a standard screw, the fine and coarse threads are easier to tighten. The coarser thread is deeper, which results in lower torques. If a screw fails because of torsional shear, it is likely to be a result of a small minor diameter.
Material
Screws have a variety of different sizes, shapes, and materials. They are typically machined on CNC machines and lathes. Each type is used for different purposes. The size and material of a screw shaft are influenced by how it will be used. The following sections give an overview of the main types of screw shafts. Each 1 is designed to perform a specific function. If you have questions about a specific type, contact your local machine shop.
Lead screws are cheaper than ball screws and are used in light-duty, intermittent applications. Lead screws, however, have poor efficiency and are not recommended for continuous power transmission. But, they are effective in vertical applications and are more compact. Lead screws are typically used as a kinematic pair with a ball screw. Some types of lead screws also have self-locking properties. Because they have a low coefficient of friction, they have a compact design and very few parts.
Screws are made of a variety of metals and alloys. Steel is an economical and durable material, but there are also alloy steel and stainless steel types. Bronze nuts are the most common and are often used in higher-duty applications. Plastic nuts provide low-friction, which helps reduce the drive torques. Stainless steel screws are also used in high-performance applications, and may be made of titanium. The materials used to create screw shafts vary, but they all have their specific functions.
Screws are used in a wide range of applications, from industrial and consumer products to transportation equipment. They are used in many different industries, and the materials they’re made of can determine their life. The life of a screw depends on the load that it bears, the design of its internal structure, lubrication, and machining processes. When choosing screw assemblies, look for a screw made from the highest quality steels possible. Usually, the materials are very clean, so they’re a great choice for a screw. However, the presence of imperfections may cause a normal fatigue failure.

Self-locking features
Screws are known to be self-locking by nature. The mechanism for this feature is based on several factors, such as the pitch angle of the threads, material pairing, lubrication, and heating. This feature is only possible if the shaft is subjected to conditions that are not likely to cause the threads to loosen on their own. The self-locking ability of a screw depends on several factors, including the pitch angle of the thread flank and the coefficient of sliding friction between the 2 materials.
One of the most common uses of screws is in a screw top container lid, corkscrew, threaded pipe joint, vise, C-clamp, and screw jack. Other applications of screw shafts include transferring power, but these are often intermittent and low-power operations. Screws are also used to move material in Archimedes’ screw, auger earth drill, screw conveyor, and micrometer.
A common self-locking feature for a screw is the presence of a lead screw. A screw with a low PV value is safe to operate, but a screw with high PV will need a lower rotation speed. Another example is a self-locking screw that does not require lubrication. The PV value is also dependent on the material of the screw’s construction, as well as its lubrication conditions. Finally, a screw’s end fixity – the way the screw is supported – affects the performance and efficiency of a screw.
Lead screws are less expensive and easier to manufacture. They are a good choice for light-weight and intermittent applications. These screws also have self-locking capabilities. They can be self-tightened and require less torque for driving than other types. The advantage of lead screws is their small size and minimal number of parts. They are highly efficient in vertical and intermittent applications. They are not as accurate as lead screws and often have backlash, which is caused by insufficient threads.